While official language condoning killer robots is shelved for now, Oakland police are still pursuing the option.
IN A SERIES of little noted Zoom meetings this fall, the city of Oakland, California, grappled with a question whose consequences could shape the future of American policing: Should cops be able to kill people with shotgun-armed robots?
The back-and-forth between the Oakland Police Department and a civilian oversight body concluded with the police relinquishing their push for official language that would have allowed them to kill humans with robots under certain circumstances. It was a concession to the civilian committee, which pushed to bar arming robots with firearms — but a concession only for the time being.
The department said it will continue to pursue lethal options. When asked whether the the Oakland Police Department will continue to advocate for language that would allow killer robots under certain emergency circumstances, Lt. Omar Daza-Quiroz, who represented the department in discussions over the authorized robot use policy, told The Intercept, “Yes, we are looking into that and doing more research at this time.”
The controversy began at the September 21 meeting of an Oakland Police Commission subcommittee, a civilian oversight council addressing what rules should govern the use of the city’s arsenal of military-grade police equipment. According to California state law, police must seek approval from a local governing body, like a city council, to determine permissible uses of military equipment or weapons like stun grenades and drones. Much of the September meeting focused on the staples of modern American policing, with the commissioners debating the permissible uses of flash-bang grenades, tear gas, and other now-standard equipment with representatives from the Oakland Police Department.
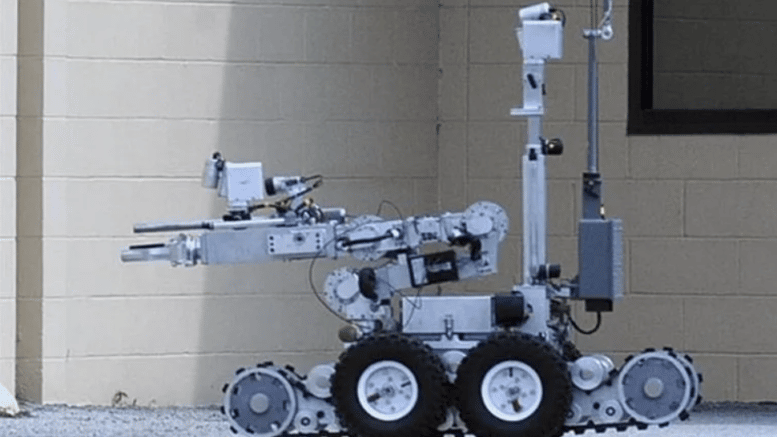
Roughly two hours into the meeting, however, the conversation moved on to the Oakland police’s stable of robots and their accessories. One such accessory is the gun-shaped “percussion actuated nonelectric disruptor,” a favorite tool of bomb squads at home and at war. The PAN disruptor affixes to a robot and directs an explosive force — typically a blank shotgun shell or pressurized water — at suspected bombs while human operators remain at a safe distance. Picture a shotgun barrel secured to an 800-pound Roomba on tank treads.
tor, Daza-Quiroz told the subcommittee that the department takes special care to ensure that it is in fact a blank round loaded into the robot’s gun. This led a clearly bemused Jennifer Tu, a fellow with the American Friends Service Committee and member of the Oakland Police Commission subcommittee on militarized policing, to ask: “Can a live round physically go in, and what happens if a live round goes in?”
“Yeah, physically a live round can go in,” Daza-Quiroz answered. “Absolutely. And you’d be getting a shotgun round.”
After a brief silence, Commissioner Jesse Hsieh asked the next question: “Does the department plan on using a live round in the robot PAN disruptor?”
The answer was immediately provocative. “No,” Daza-Quiroz said, before quickly pivoting to hypothetical scenarios in which, yes, just such a shotgun-armed robot might be useful to police. “I mean, is it possible we have an active shooter in a place we can’t get to? And he’s fortified inside a house? Or we’re trying to get to a person —”
IT SOON BECAME clear the Oakland Police Department was saying what nearly every security agency says when it asks the public to trust it with an alarming new power: We’ll only use it in emergencies — but we get to decide what’s an emergency.
The question of whether robots originally designed for defusing bombs should be converted into remote-controlled guns taps into several topics at the center of national debates: police using lethal force, the militarization of American life, and, not least of all, killer robots. Critics of the armed robo-cops note that the idea of Predator drones watching American racial justice protests may have seemed similarly far-fetched in the years before it started happening. “It’s not that we don’t want to debate how to use these tools safely,” said Liz O’Sullivan, CEO of the AI bias-auditing startup Parity and a member of the International Committee for Robot Arms Control. “It’s a question of, if we use them at all, what’s the impact going to be to democracy?”
Some observers say the Oakland police’s robot plan contradicts itself. “It’s billed as a de-escalation facilitator, but they want to keep it open as a potential lethal weapon,” Jaime Omar Yassin, an independent journalist in Oakland who has documented the commission meetings, tweeted. As with any high-tech toy, the temptation to use advanced technology may surpass whatever institutional guardrails the police have in place. Matthew Guariglia, a policy analyst with the Electronic Frontier Foundation, said, “The ease of use of weapons as well as the dangerous legal precedence justifying the casual use of weapons makes police less likely to attempt to deescalate situations.”
“It in many ways lowers the psychological hurdle for enacting that violence when it’s just a button on a remote control.”
Tu hopes that by cracking down on shotgun robots before they come to be, Oakland and cities across the country can avoid debates about limits on police powers that only come after those powers are abused. She pointed to the Oakland police ban on using firehoses, a bitter reminder of abuses in American policing from the not-too-distant past. “We have an opportunity right now to prevent the lawsuit that will force the policy to be rewritten,” Tu said. “We have an opportunity to prevent the situation, the harm, the trauma that would occur in order for a lawsuit to need to be initiated.”
Skeptics of robo-policing, including Tu, say these debates need to happen today to preempt the abuses of tomorrow, especially because of the literal and figurative distance robotic killing affords. Guariglia said, “It in many ways lowers the psychological hurdle for enacting that violence when it’s just a button on a remote control.”
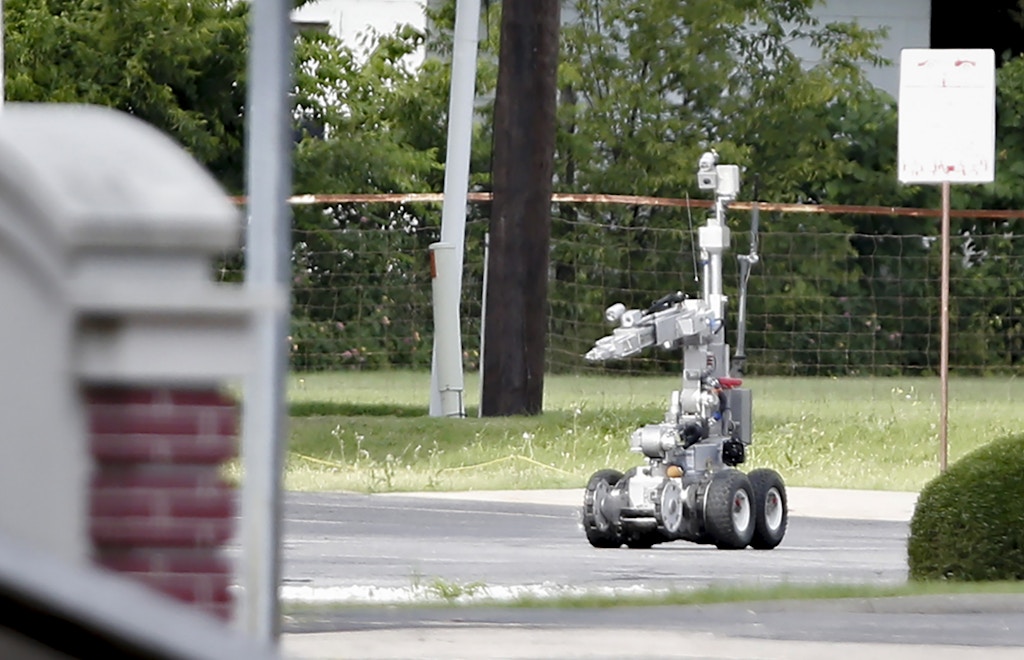

Oakland police are seeking to use live shotgun rounds in an attachment to the Remotec Adros Mark V-A1, a robot seen here in a standoff where Dallas police deployed the robot in Dallas, Texas, on June 13, 2015.
Photo: Stewart F. House/Getty Images
AS THE OAKLAND commission hearing went on, Daza-Quiroz invoked a controversial 2016 incident in Dallas. Police had strapped a C-4 bomb to a city-owned robot and used it to blow up a sniper who’d killed five police officers during a downtown rally. It is widely considered to be the country’s first instance of robotic police killing. While police generally heralded the ingenuity of the response, others criticized it as summary execution by robot. In an email to The Intercept, Daza-Quiroz said the department imagines weaponizing the PAN disruptor on the department’s $280,000 Northrop Grumman Remotec Andros Mark 5-A1 robot — the very same model used so controversially in Dallas.
Daza-Quiroz noted that the department had never actually attempted to load a live round into the PAN gun for fear of breaking the $3,000 attachment. Yet when Tu asked whether the commission could add policy language that would prohibit arming the robot with lethal 12-gauge shotgun rounds, the department’s vision for robotic policing became clearer. “I don’t want to add a prohibited use,” Daza-Quiroz replied, “because what if we need it for some situation later on?”
Daza-Quiroz explained that a hypothetical lethally armed robot would still be subject to the department’s use of force policy. Oakland Police Department Lt. Joseph Turner, stressing the need to keep extreme options on the table for extreme circumstances, urged the commission to allow such a killer robot in case of “exigencies.” He said, “I’m sure those officers that day in Texas did not anticipate that they were going to deliver a bomb using a robot.”
The Oakland Police Department’s assurances that a shotgun-toting robot would be subject to departmental use-of-force policy did not seem to satisfy critics. Nor did the messenger have a record that inspires confidence. A 2013 East Bay Express report on Daza-Quiroz and another officer’s killing of an unarmed Oakland man found that he had been the subject of over 70 excessive force complaints. (One lawsuit prompted a six-figure settlement from the city and the jury ruled for the officers in another; the officers were never charged with a crime, and an arbitrator overturned the police chief’s decision to discipline the officers. Police spokesperson Candace Keas declined to comment on the dozens of excessive force complaints.)
In the wake of the shooting, which prompted protests, the East Bay Times reported that Daza-Quiroz was asked by an internal investigator why he hadn’t used his Taser instead. He responded, “I wanted to get lethal.”
“You have a hammer, everything looks like a nail.”
The concern is, then, less that police would use a shotgun robot in “certain catastrophic, high-risk, high-threat, mass casualty events” — as the tentative policy language favored by the department currently reads — but that such a robot would be rolled out when the police simply want to get lethal. The vagaries of what precisely constitutes a “high-risk” event or who determines the meaning of “high threat” affords the police too much latitude, Tu told The Intercept in an interview. “It’s not a technical term, there’s no definition of it,” she said. “It doesn’t mean anything.” When asked by email for precise definitions of these terms, Daza-Quiroz said, “High risk, high threat incidents can vary in scope and nature and are among the more challenging aspects of law enforcement.”
Critics say such ambiguous language means Oakland police would get to use a robot to kill someone whenever they decide they need a robot to kill someone. The policy has analogues in more routine police work: After shooting unarmed people, officers frequently offer post-hoc justifications that they felt their life was in danger.
“Anytime anyone has a tool, they’re going to use it more,” said Tu. “You have a hammer, everything looks like a nail. And the more that police, in general, have military equipment, have more weapons, those weapons get used.”
AFTER WEEKS OF wrangling, both the commission and the police department agreed on language that will prohibit any offensive use of robots against people, with an exception for delivering pepper spray. The agreement will go for review by the city council on October 18.
Tu suspects the sudden compromise on the killer-robot policy is explained not by any change of heart, but rather by the simple fact that had the debate continued any longer, the department would have missed the deadline for submitting a policy — and risked losing the ability to legally operate its robots altogether.
There is nothing preventing the Oakland Police Department from, as Daza-Quiroz said they will, continuing to push for legally sanctioned killing using a PAN disruptor. No matter how the Oakland policy shakes out in the long term, the issue of robotic policing is likely to remain. “I’m sure Dallas [police] weren’t the only ones who had considered lethal force with their robot before doing so, and Oakland police aren’t the only ones who are thinking about it even more now,” Tu told The Intercept. “They’re just the only ones who thought about it out loud with a committee.”
According to Daza-Quiroz, the department is still looking toward the future. “We will not be arming robots with lethal rounds anytime soon, and if, and when that time comes each event will be assessed prior to such deployment,” he said. When asked if there were other situations beyond a Dallas-style sniper in which police might wish to kill with a robot, Daza-Quiroz added: “Absolutely there are many more scenarios.”
With thousands of Andros robots operated by hundreds of police department across the country, those concerned by the prospect of shotgun robots on the streets of Oakland or elsewhere refer to what they say is a clear antecedent with other militarized hardware: mission creep.
“We’re not really talking about a slippery slope. It’s more like a well-executed playbook to normalize militarization.”
Once a technology is feasible and permitted, it tends to linger. Just as drones, mine-proof trucks, and Stingray devices drifted from Middle Eastern battlefields to American towns, critics of the PAN disruptor proposal say the Oakland police’s claims that lethal robots would only be used in one-in-a-million public emergencies isn’t borne out by history. The recent past is littered with instances of technologies originally intended for warfare mustered instead against, say, constitutionally protected speech, as happened frequently during the George Floyd protests.
“As you do this work for a few years, you come to realize that we’re not really talking about a slippery slope. It’s more like a well-executed playbook to normalize militarization,” said O’Sullivan, of Parity. There’s no reason to think the PAN disruptor will be any different: “One can imagine applications of this particular tool that may seem reasonable, but with a very few modifications, or even just different kinds of ammunition, these tools can easily be weaponized against democratic dissent.”



More Stories
Today’s News: March 26, 2024
The Greatest Purveyor of Violence In The World
Video: Fred Dashevsky – The CPI Fallacy